We’re thrilled to announce a new title from Clint Warren-Davey para el programa P-300 de Neva Wargames.
Many of you have asked about our focus on 1-2 player wargames, wondering, “"¿Y dónde están los títulos multijugador?” While we’ve announced one 1-4 player title so far, we know that’s not enough—we’re finally closing that gap! Preparaos: ¡un nuevo juego multijugador se une ahora a nuestro programa P300!
El aspecto visual es provisional, aún no se ha asignado diseñador gráfico, pero estamos trabajando en ello en estos momentos. Se esperan novedades muy pronto.
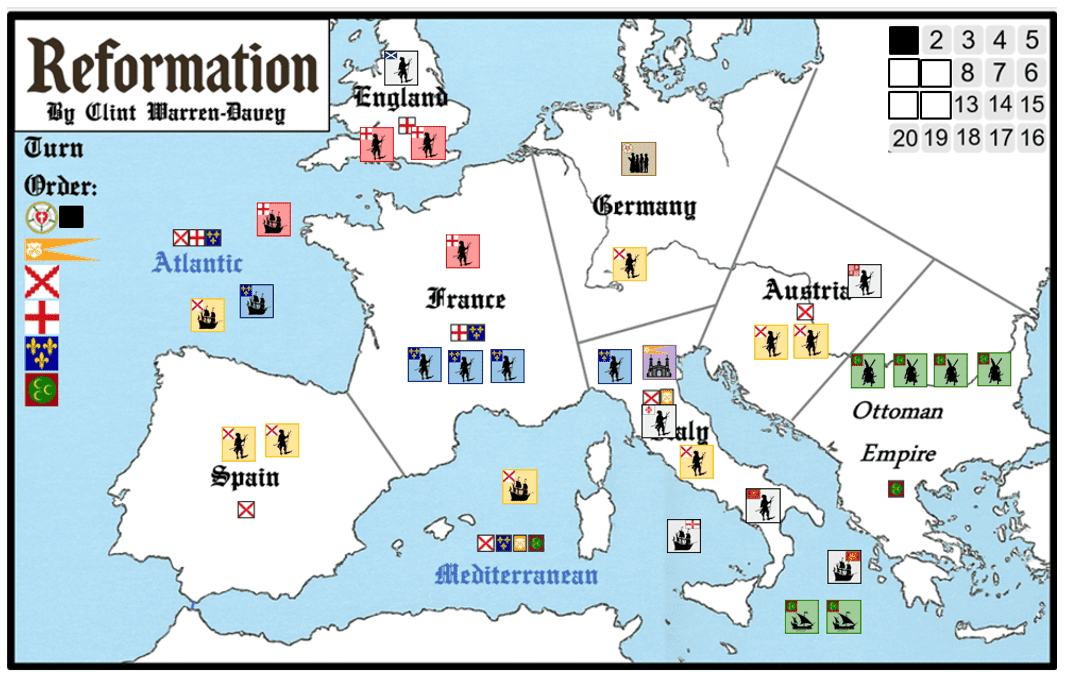
MODERN | STRATEGIC | 2-6 PLAYERS | DURATION 60-90′
DISEÑO: CLINT WARREN-DAVEY
Reforma: Fuego y fe Es un juego sobre las guerras y luchas religiosas que asolaron Europa desde 1517 hasta 1555. Este periodo fue testigo de la Reforma Protestante, iniciada por el monje renegado Martín Lutero, y las subsiguientes guerras de religión en Alemania y otros lugares, que sacudieron al cristianismo hasta sus cimientos. La época también estuvo marcada por numerosas guerras entre las grandes potencias europeas, independientemente de su afiliación religiosa. El Imperio Otomano estaba en su apogeo y amenazaba el mundo cristiano desde el sureste, mientras que, al mismo tiempo, se descubrían nuevas tierras en las Américas, iniciando una carrera por la expansión colonial. En este juego, de 2 a 6 jugadores utilizarán sus Ejércitos, Flotas, Seguidores e Iglesias en un intento por lograr sus condiciones de victoria y obtener la mayor cantidad de Puntos de Victoria (PV). La duración es de aproximadamente 60-90 minutos. Las reglas son muy sencillas y fáciles de enseñar, ya que el juego fue diseñado originalmente para su uso en un entorno de escuela secundaria por el profesor y diseñador de juegos altamente experimentado, Clint Warren-Davey. El juego incluye 6 Facciones únicas que compiten por el dominio, cada una a su manera:

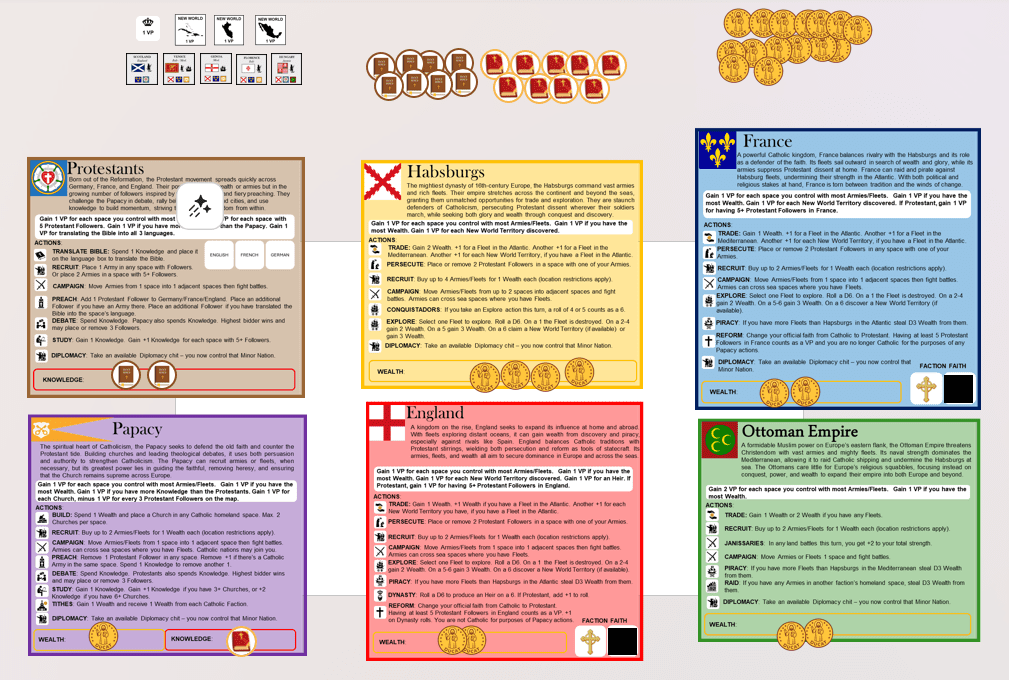
Protenstantes Son una facción religiosa que se extenderá rápidamente por Alemania, Francia e Inglaterra. Su poder no reside en la riqueza o los ejércitos, sino en el creciente número de seguidores, inspirados por las Biblias traducidas y la predicación apasionada. Desafían al Papado en debate, reúnen creyentes en ciudades y pueblos, y utilizan el conocimiento para generar impulso, esforzándose por reformar la Cristiandad desde dentro.

Papado Es el corazón espiritual del Catolicismo, y su misión es defender la antigua fe y contrarrestar la marea protestante. Construyendo iglesias y liderando debates teológicos, utiliza tanto la persuasión como la autoridad para fortalecer el Catolicismo. El Papado puede reclutar ejércitos o flotas cuando sea necesario, pero su mayor poder reside en guiar a los fieles, erradicar la herejía y asegurar que la Iglesia mantenga su supremacía en toda Europa.

Hasburgo son la dinastía más poderosa de la Europa del siglo XVI, con un control total sobre ejércitos masivos y ricas flotas. Su imperio se extiende por todo el continente y más allá de los mares, dándoles oportunidades inigualables de comercio y exploración. Son firmes defensores del Catolicismo, persiguiendo la disidencia protestante dondequiera que sus soldados marchen, mientras buscan gloria y riqueza a través de la conquista y el descubrimiento.

Inglaterra es un reino en pleno ascenso, que busca expandir su influencia tanto en casa como en el extranjero. Con flotas que exploran océanos distantes, puede obtener riqueza mediante el descubrimiento y la piratería, especialmente contra rivales como la España de los Habsburgo. Inglaterra equilibra las tradiciones Católicas con los crecientes movimientos Protestantes, utilizando tanto la persecución como la reforma como herramientas de Estado. Sus ejércitos, flotas y riqueza apuntan a asegurar el dominio en Europa y a través de los mares.

Francia es un poderoso reino Católico que equilibra su feroz rivalidad con los Habsburgo y su papel como defensor de la fe. Sus flotas navegan en busca de riqueza y gloria, mientras sus ejércitos reprimen la disidencia Protestante en casa. Francia puede llevar a cabo incursiones y actos de piratería contra las flotas de los Habsburgo, socavando su fuerza en el Atlántico. Con intereses tanto políticos como religiosos en juego, Francia está dividida entre la tradición y los vientos de cambio.

Imperio Otomano is a formidable Muslim power on Europe’s eastern flank, threatening Christendom with vast armies and mighty fleets. Its naval strength dominates the Mediterranean, allowing it to raid Catholic shipping and undermine the Habsburgs at sea. The Ottomans care little for Europe’s religious squabbles, focusing instead on conquest, power, and wealth to expand their empire into both Europe and beyond.
Wishlist “Reformation: Fire and Faith Damos el pistoletazo de salida pruebas de juego pronto en nuestro servidor Discord. Si estás interesado en ser uno de los primeros en experimentar el juego y ayudar a dar forma a su desarrollo, únete a nuestra comunidad de Discord aquí and head over to the #reformation section to let us know!